Techno-option Case Study: Voltas
Technical Analysis provides traders with a sense of direction, while option strategies enable them to execute orders in multiple ways. When these two approaches are combined, traders can gain an added edge. To better understand the benefits of this combination, let’s examine a real-time case study on Voltas.
Chart 1: Nifty Daily
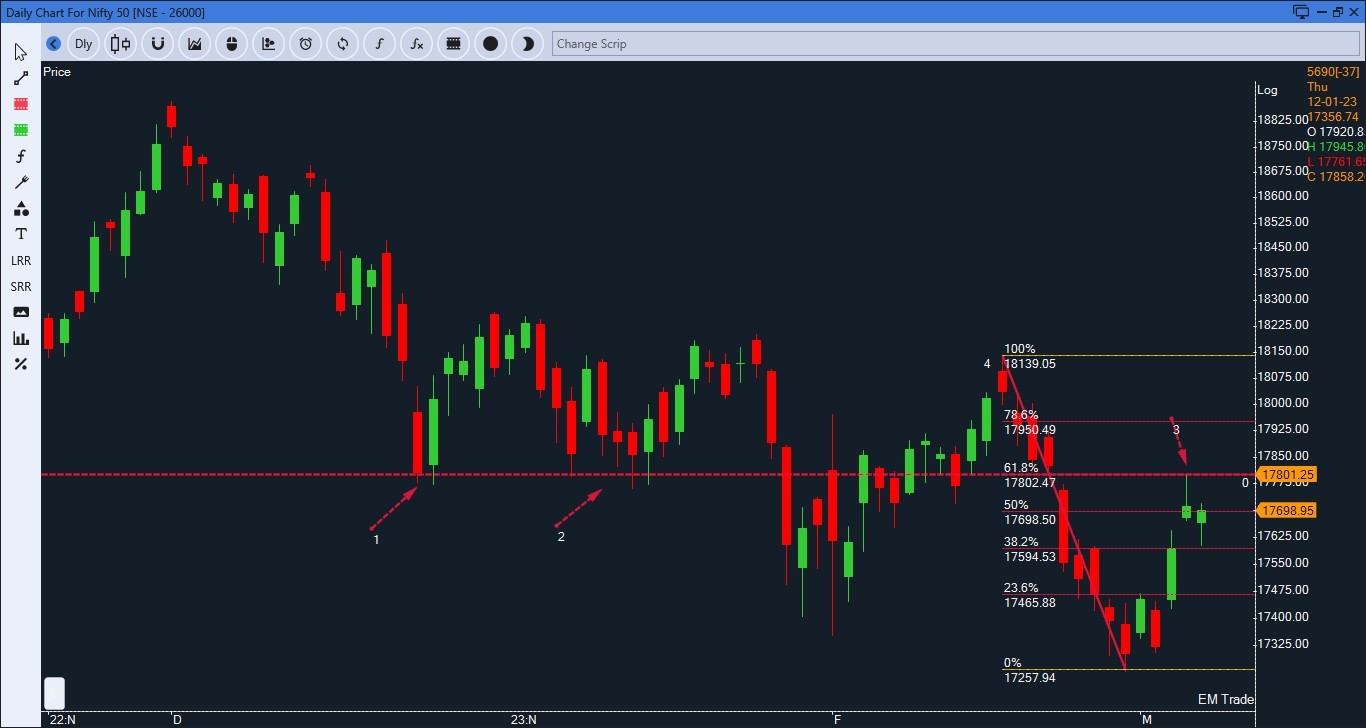
Over the past three months, the index has been on a declining trend. In this negative trend, resistance has proven to be stronger than support. While the index recently saw a 3% upside move, it is currently hovering around the resistance level which coincides with the 61.8% retracement level. The formation of a large wick at the resistance level indicates the presence of sellers, which is a potential weak sign.
In such situations, it is advisable to look for weak sectors or stocks that are at resistance levels. Recently, consumer durable stocks, including consumer electronics, have not performed well. For this case study, we will focus on Voltas as it has underperformed in the market. Although the stock has seen a recent upside move, it is currently around the resistance level.
Let’s examine the chart for Voltas. Despite its negative movement, the stock has risen 25% and reached a strong resistance level of 930. This level coincides with a stiff horizontal line, a downward-sloping moving average(it indicates prices have been constantly giving lower closing), and the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level. Fibonacci tools help you figure quick pivot points on the chart where prices might probably change trend.
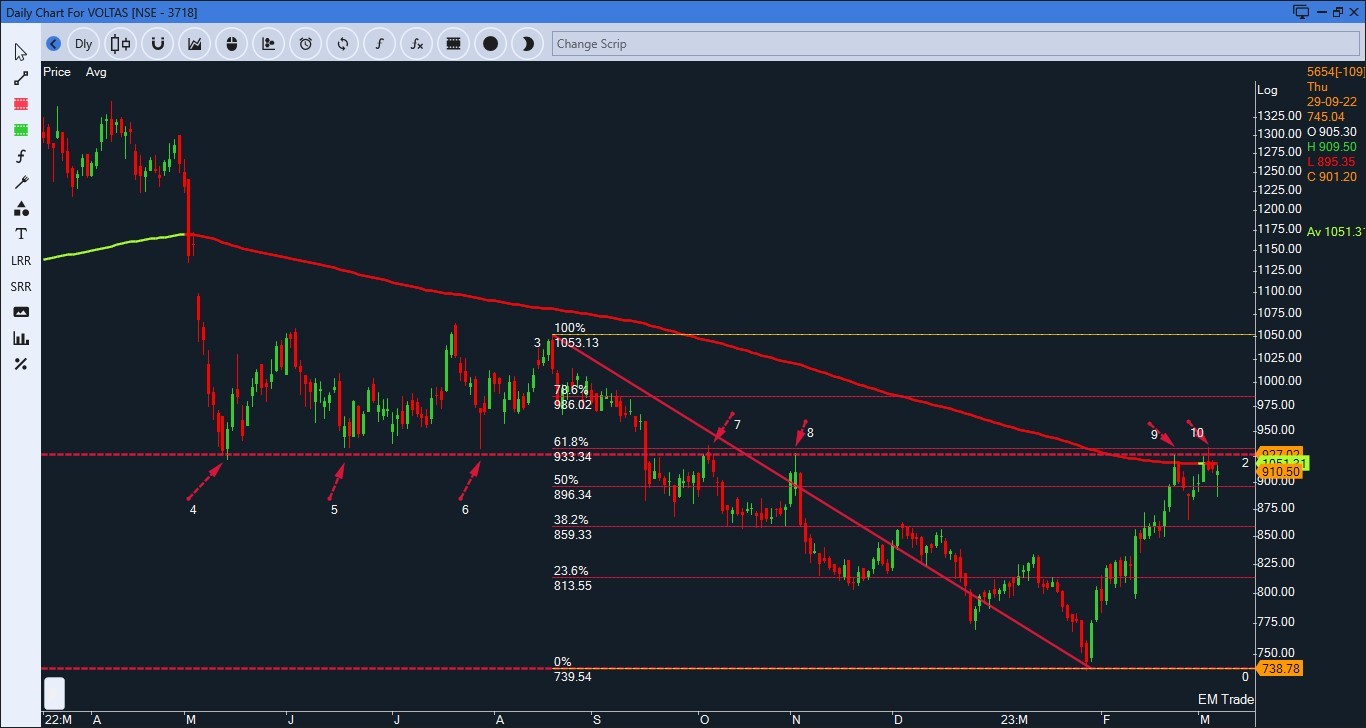
Based on this analysis, we can conclude that Voltas is in a negative trend with a stiff resistance level at 930. To trade this view, one can either short futures or buy put options. However, this is a plain vanilla way to trade and comes with its perils, such as the need for a large margin. In the case of Voltas, the required margin is more than 1 lakh, and the lot size is 600 quantities. This means that even a 1% move in the stock can cause a fluctuation of Rs 6,000 in the profit and loss (P&L) of the trader.
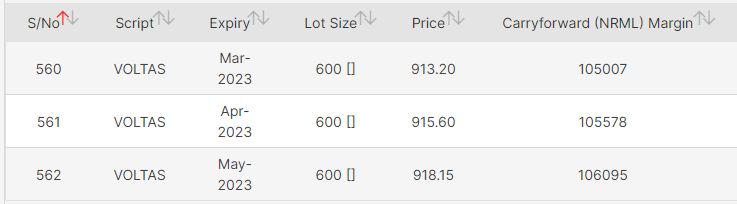
In addition to the margin, traders must maintain mark-to-market (MTM) calculations, which involve the daily settlement of profits and losses based on the closing price of the security. This can be a high-risk proposition for retail traders with limited experience and risk appetite.
My recommendation is that traders with decent experience, risk appetite, and deep pockets may prefer equity futures trading. Those who want to gain hands-on experience with futures trading can explore commodities mini-series contracts or currency futures.
Another way to execute the trade is to buy put options. The adage for options buying is “limited loss and unlimited profit.” However, over time, traders realize that options buying can be a silent killer due to time decay. It has been observed that a majority of options expire worthless.
My recommendation is that options buyers should avoid out-of-the-money or deep out-of-the-money options, as their premium does not move along with the stock price, and their premium shrinks substantially due to time decay.
Option strategies offer greater flexibility in architecting trading strategies based on risk and market outlook.
To execute a bearish or not-so-bullish view on Voltas, there are various strategies to choose from, such as credit spreads (receive money by selling options) and debit spreads (pay money to buy options). Typically, credit spread strategies are preferred as time decay in options works in favor of the seller.
For our case, we have chosen the Bear Call Spread strategy to execute our view on Voltas. A Bear Call Spread is a two-legged options strategy used when the market outlook is moderately bearish. This strategy involves creating a spread by selling call options for credit.
In our case, as Voltas is currently hovering around its resistance level after a 25% upside move, the call option premium is likely to be inflated, allowing the option seller to earn a healthy premium.
To implement the Bear Call Spread strategy, follow these steps:
Buy 1 Out of The Money (OTM) Call option (leg 1).
Sell 1 In The Money (ITM) Call option (leg 2).
Make sure that both options belong to the same underlying asset, same expiry series, and that each leg involves the same number of options.
For our case, we will buy the Voltas 950 CE at a premium of 9.75 and sell the 920 CE at a premium of 19.5, as of 08.03.23
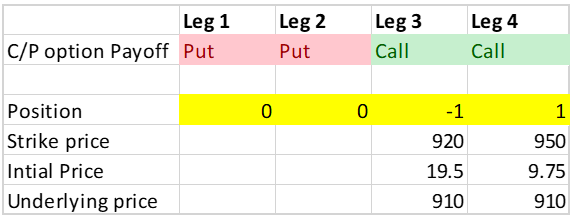
Basic calculation of option strategy
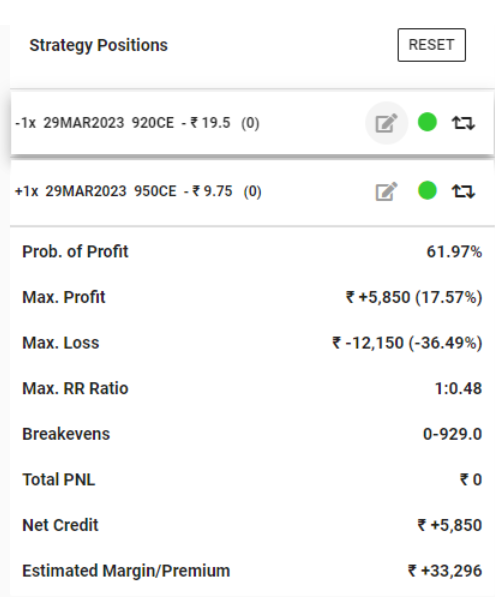
By inserting the strategy, we get basic calculations. Courtesy to Opstra
Payoff Table
| Underlying price | Leg 1 | Leg 2 | Leg 3 | Leg 4 | Combined |
| 890 | 0 | 0 | 11700 | -5850 | 5850 |
| 900 | 0 | 0 | 11700 | -5850 | 5850 |
| 910 | 0 | 0 | 11700 | -5850 | 5850 |
| 920 | 0 | 0 | 11700 | -5850 | 5850 |
| 930 | 0 | 0 | 5700 | -5850 | -150 |
| 940 | 0 | 0 | -300 | -5850 | -6150 |
| 950 | 0 | 0 | -6300 | -5850 | -12150 |
| 960 | 0 | 0 | -12300 | 150 | -12150 |
| 970 | 0 | 0 | -18300 | 6150 | -12150 |
The payoff table shows the potential profit or loss for every possible strike price of an option while considering its expiration date. In this specific strategy, the maximum profit achievable is 5850, while the maximum loss could be 12150. The risk-to-reward ratio of this strategy is 1:0.48, which means that the potential loss is almost twice the potential profit.
It is reasonable to question why someone would choose to employ a strategy with such a high potential loss and relatively low potential profit. However, when evaluating an option strategy, one must consider not only the risk-to-reward ratio but also the probability of profit (PoP). In this instance, the strategy was designed to take advantage of a moderately bearish view of Voltas. By implementing a defensive bear call spread strategy, the trade can be profitable if Voltas’ price closes below the 930 level at the time of expiry.
Performing technical analysis and utilizing option strategies allow for a customized approach that matches the desired level of risk and view on a particular trade. By implementing this strategy, we can see at the end of the expiry how it fared in practice.





